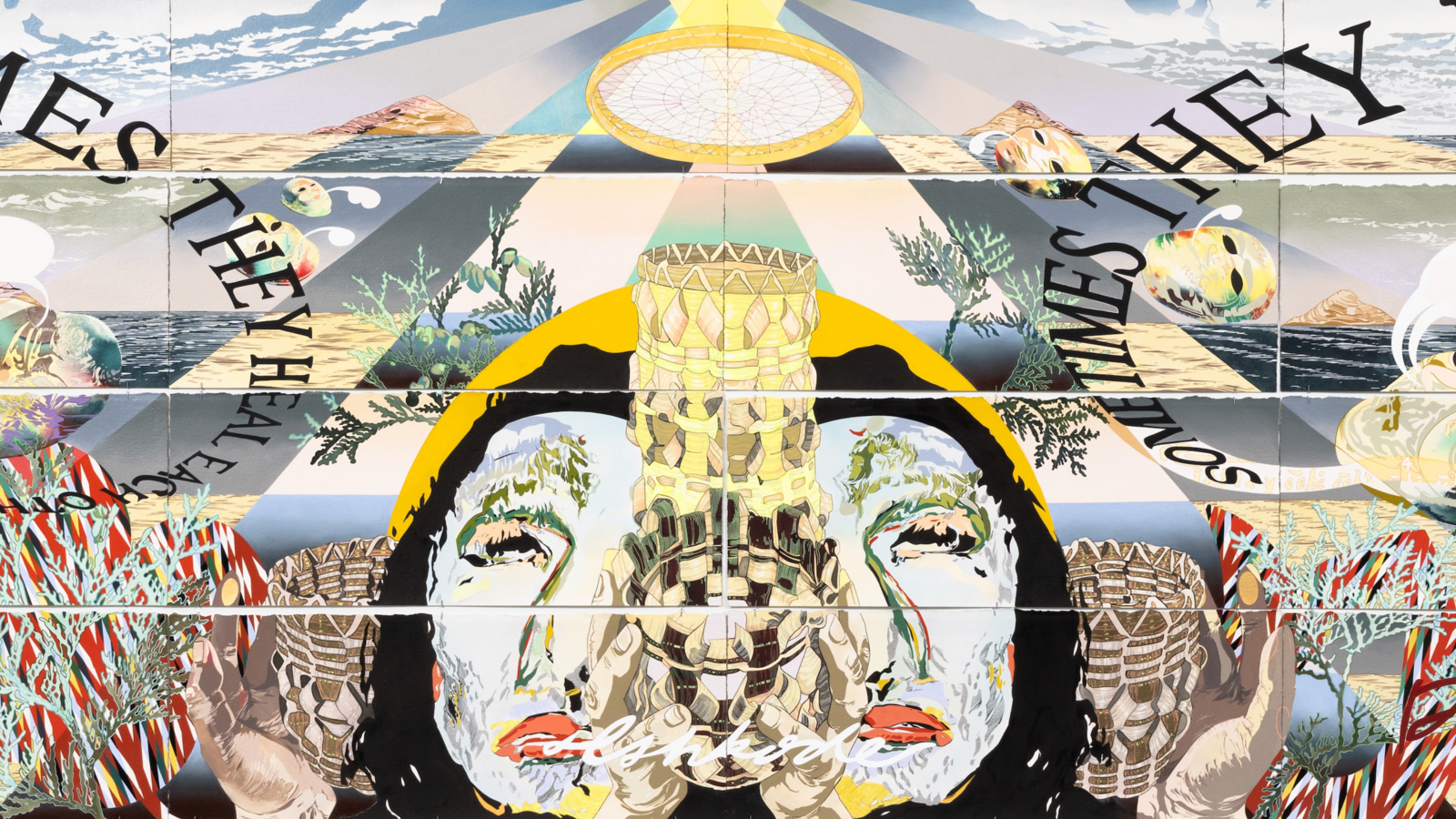
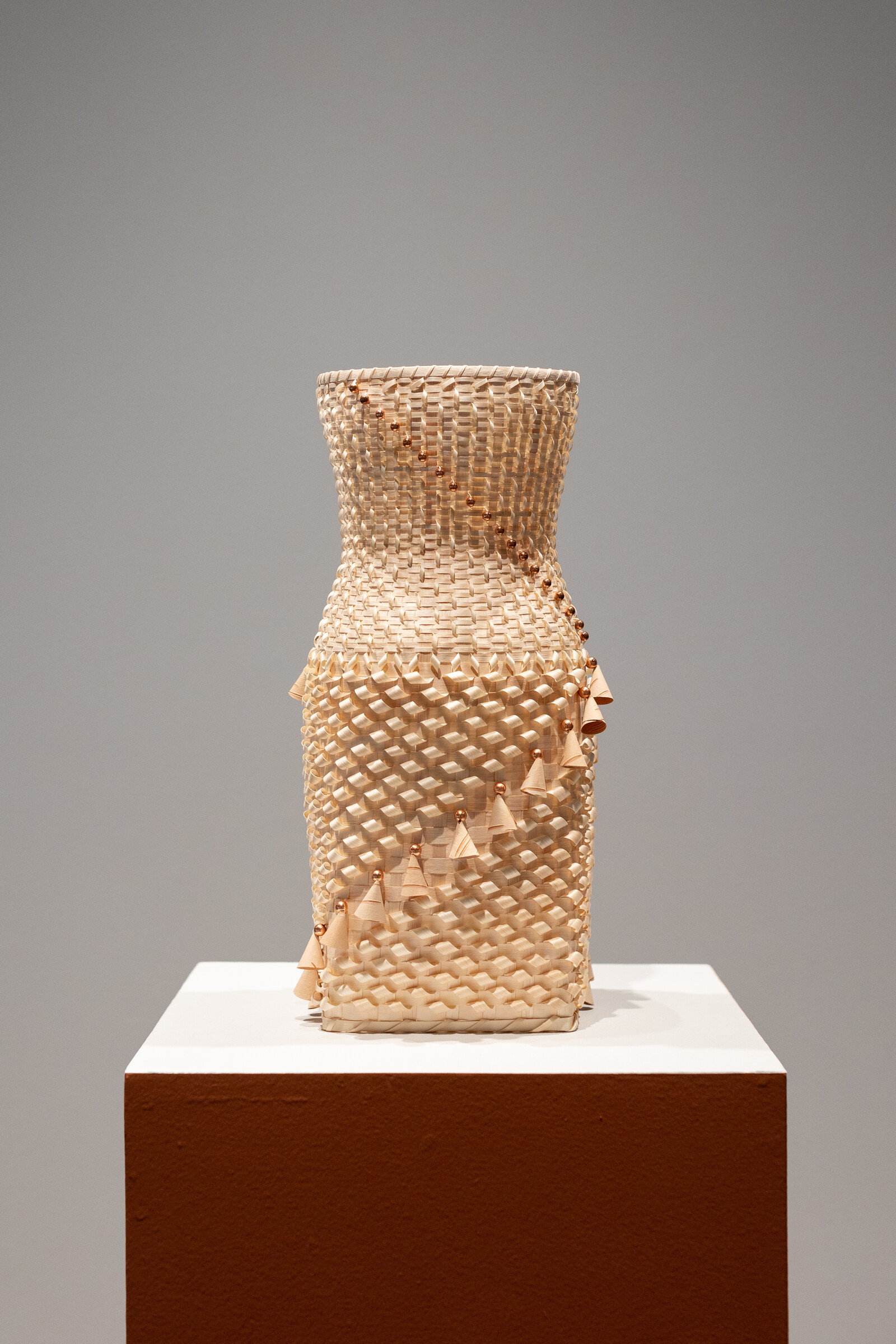
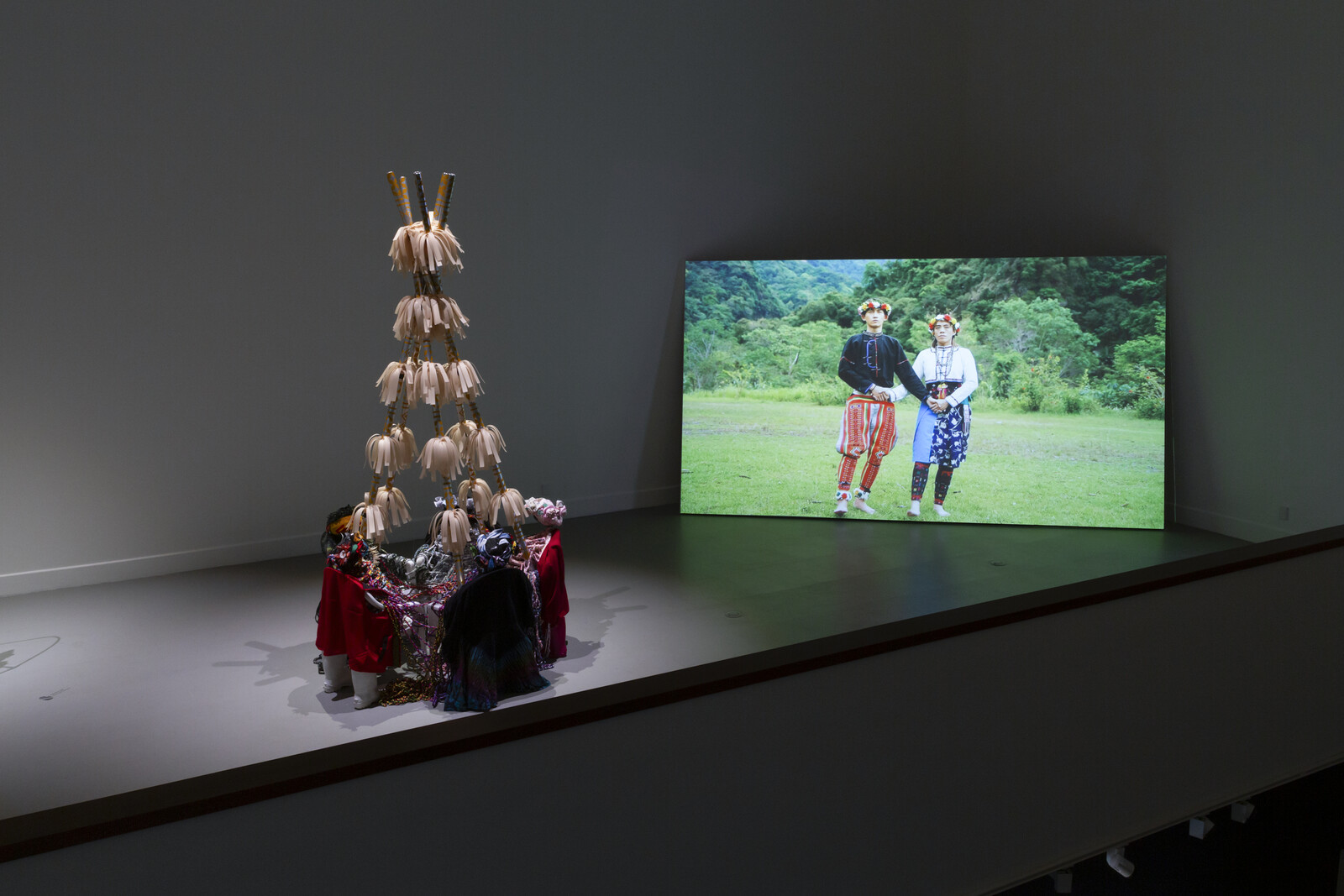
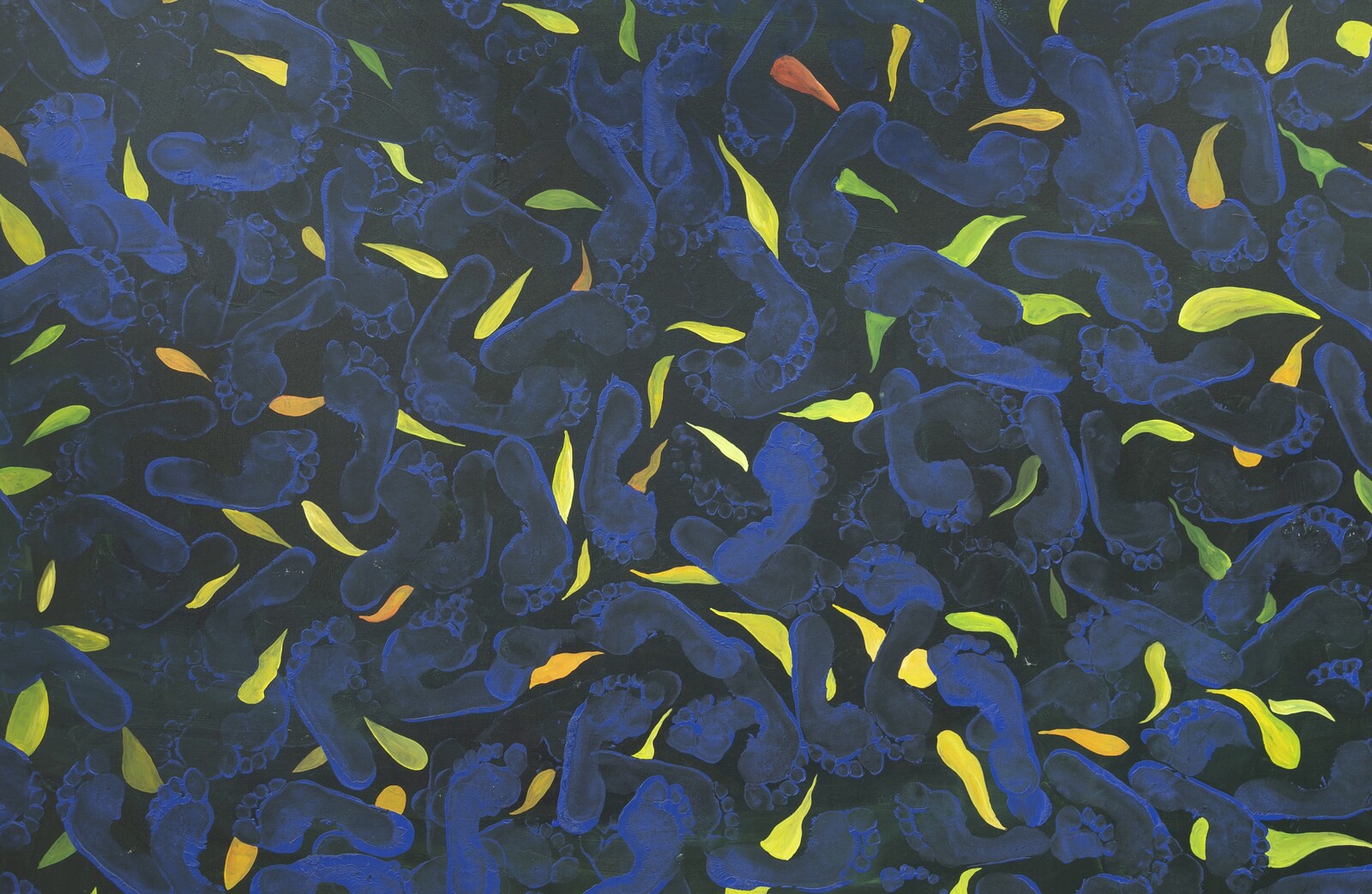
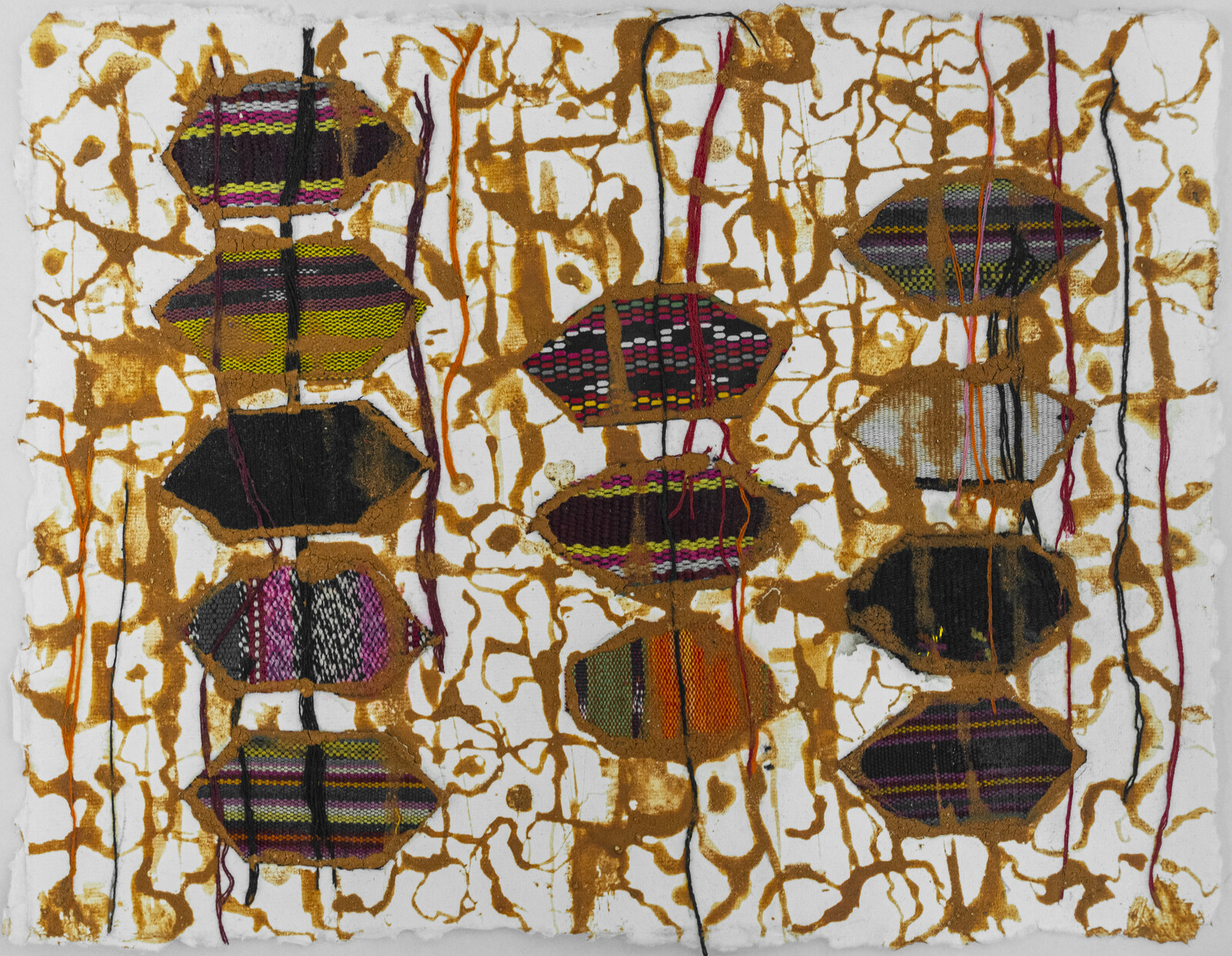
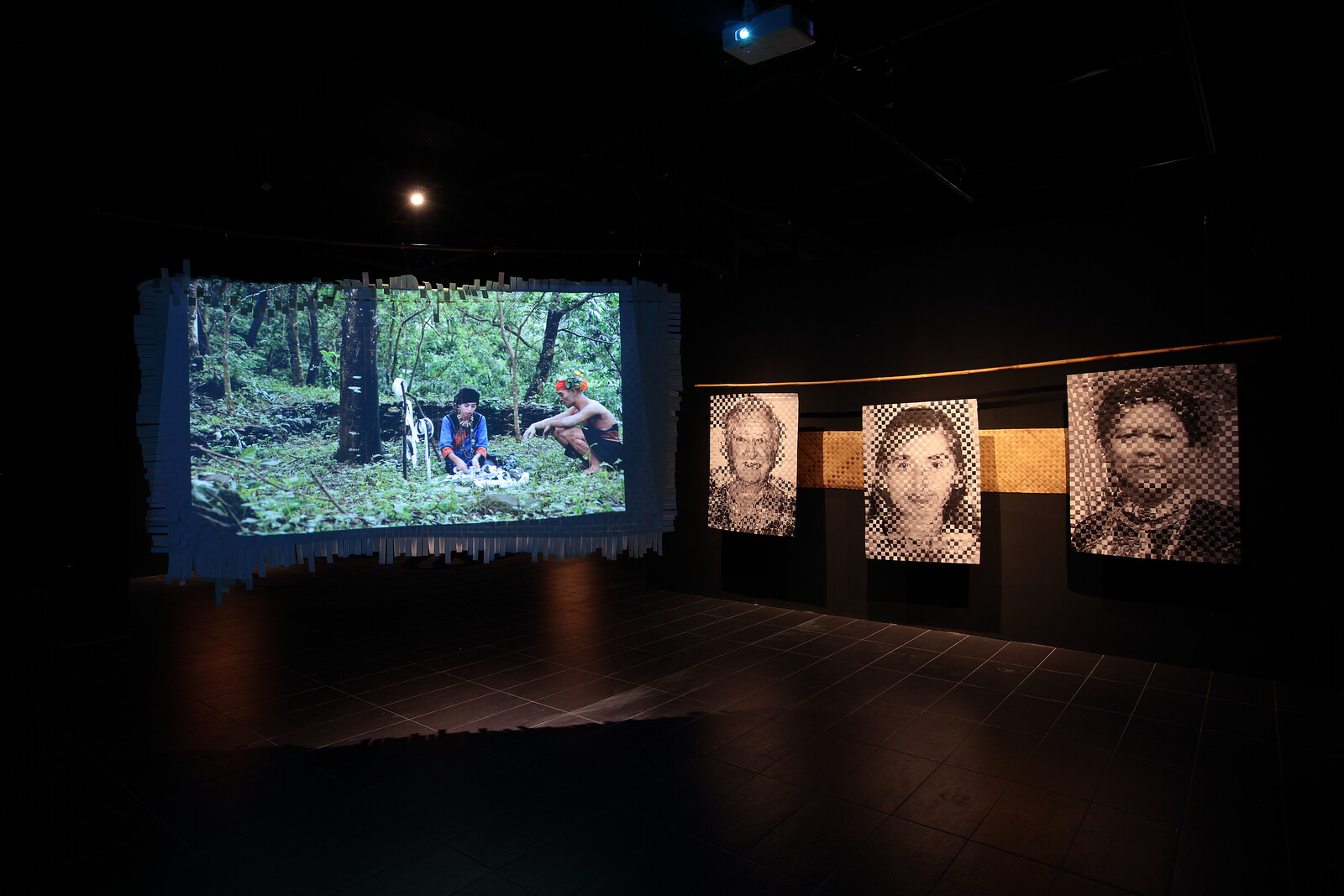
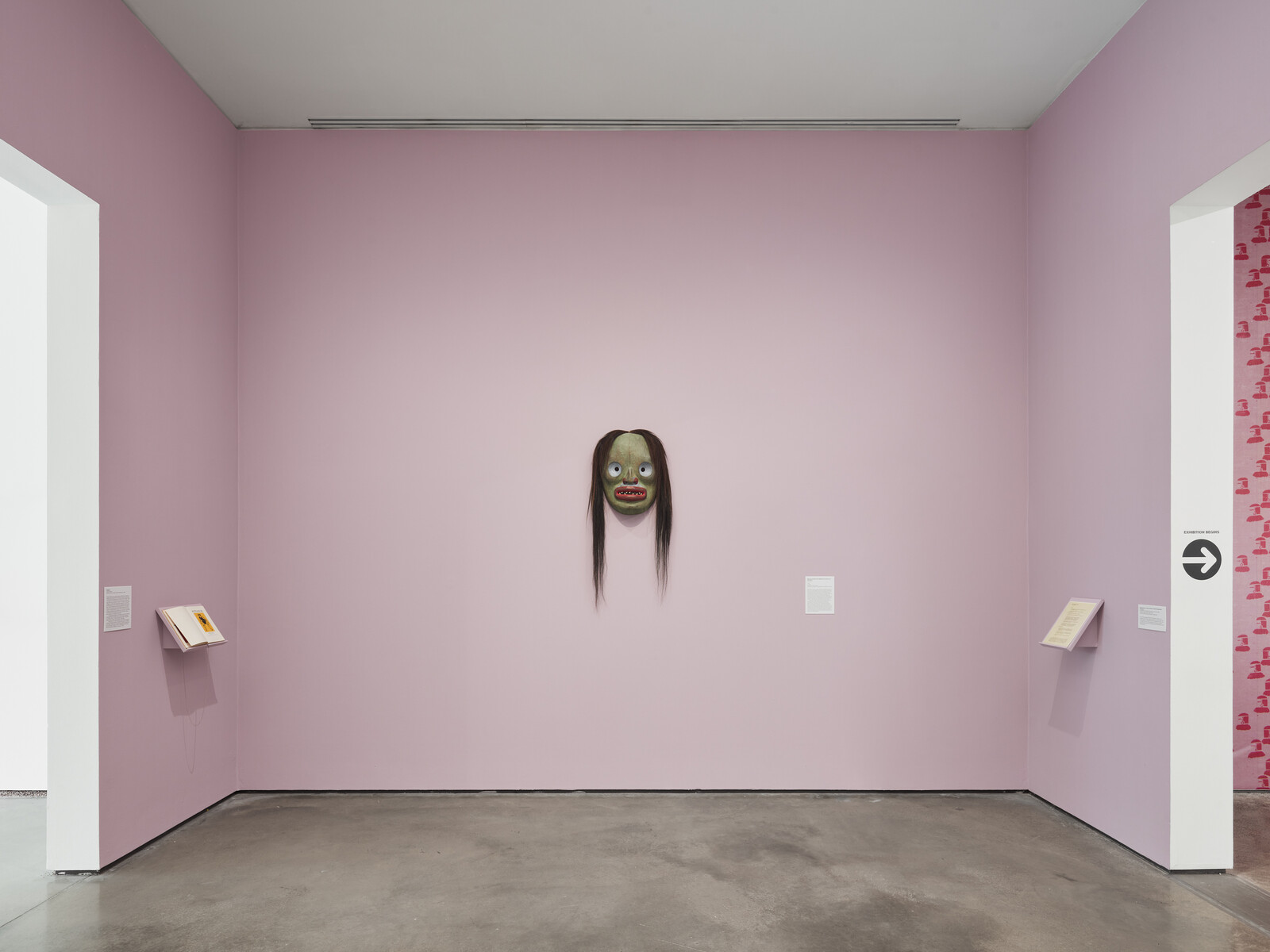
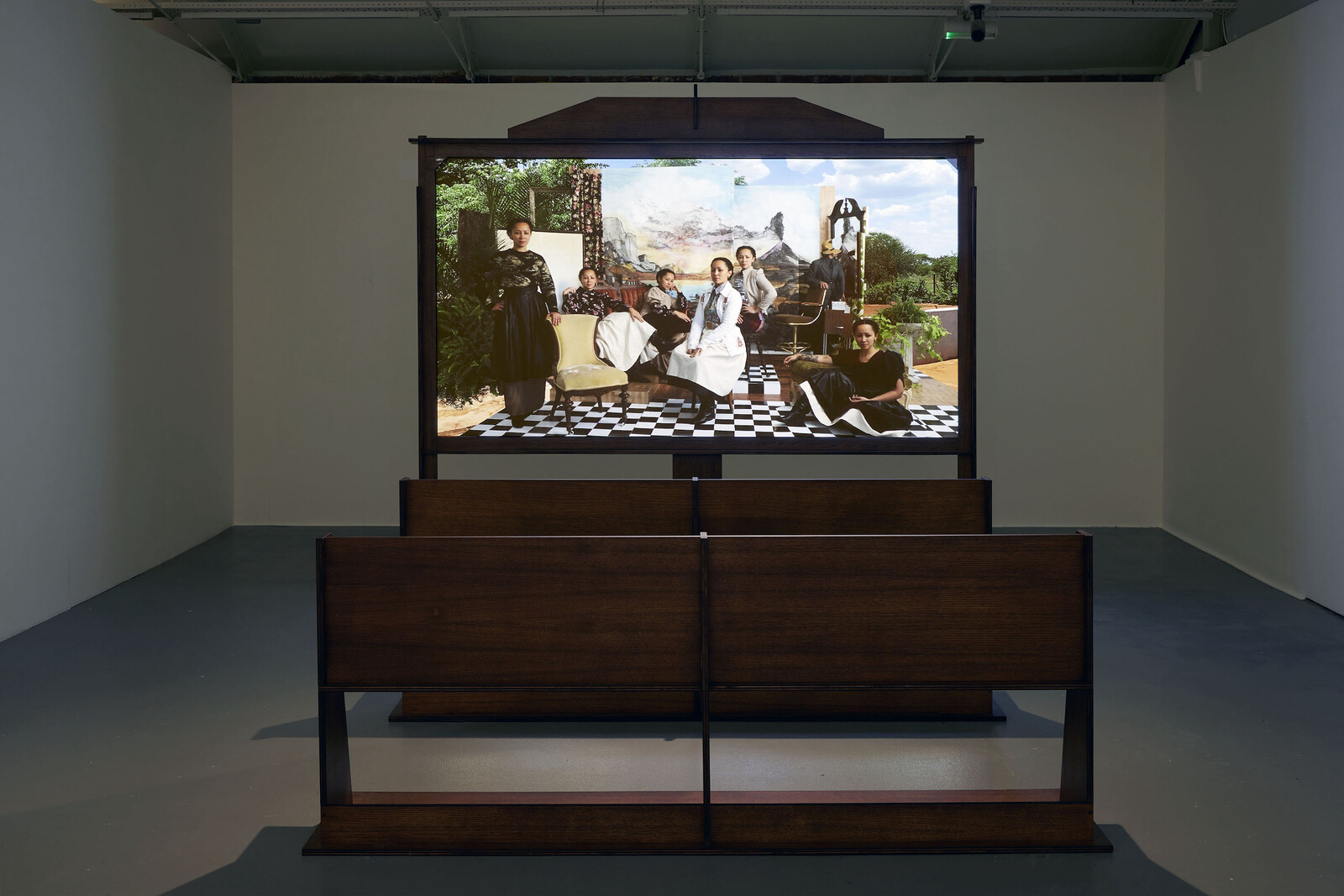
Textiles express ancestral knowledge of geometry and mathematics connected to the Mayan worldview, incorporating elements of politics, nature, history, and memory. Each community has different colors, embroideries, and figures that have been passed down from generation to generation. As the slogan of the National Movement of Women Weavers says: “The weavings are the books that colonialism could not burn.”
If many in the West today have the sense that the world is coming to an end, it is very much their world that is ending; other worlds were invaded and ripped apart long ago, yet the peoples in question refused to disappear—or, as with the Creole populations of the Caribbean, they became an unprecedented people spanning several aboriginal pasts, the long present of (neo)colonialism, and uncertain futures. Meanwhile the extractivist machine keeps accelerating—even amidst the symptoms of planetary collapse. The million-dollar question—to use an inappropriate metaphor—is to what extent contemporary forms of asymmetrical schismogenesis can maintain or produce forms of life in opposition to financialized and racialized capitalism.